The Role of Agentic AI in Transforming Healthcare and Life Sciences
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is entering a new phase—one that goes beyond chatbots and task automation. The rise of Agentic AI marks a turning point where intelligent systems don’t just respond to prompts but autonomously execute multi-step processes, orchestrate workflows, and collaborate with humans to drive real outcomes.
In no industry is this transformation more impactful than in healthcare and life sciences, where complex data, regulatory challenges, and the high cost of error have long slowed innovation. Agentic AI has the potential to shift this ecosystem from reactive, inefficient “sick care” to proactive, data-driven, outcome-based healthcare.
From Reactive Systems to Intelligent Orchestration
Today’s healthcare systems still operate largely as “sick care”—reactive rather than preventive. Despite tremendous advances in digital health, inefficiencies remain widespread due to regulatory caution, data silos, and manual processes.
Subject-matter experts like clinicians, researchers, and medical operations leads often have transformative ideas but lack the technical resources to bring them to life. Overworked IT teams prioritize only a few enterprise projects each year, leaving innovation bottlenecked.
This is the gap Agentic AI in healthcare aims to close. By allowing non-technical users to describe workflows in plain English, agentic systems can automatically assemble AI-native, production-grade applications behind the scenes. These platforms represent a major leap from traditional low-code or no-code AI tools, which were limited to building simple interfaces. With Agentic AI, domain experts can now design complex, compliant, and scalable workflows—without writing a single line of code.
How Agentic AI Works: From LLMs to Action
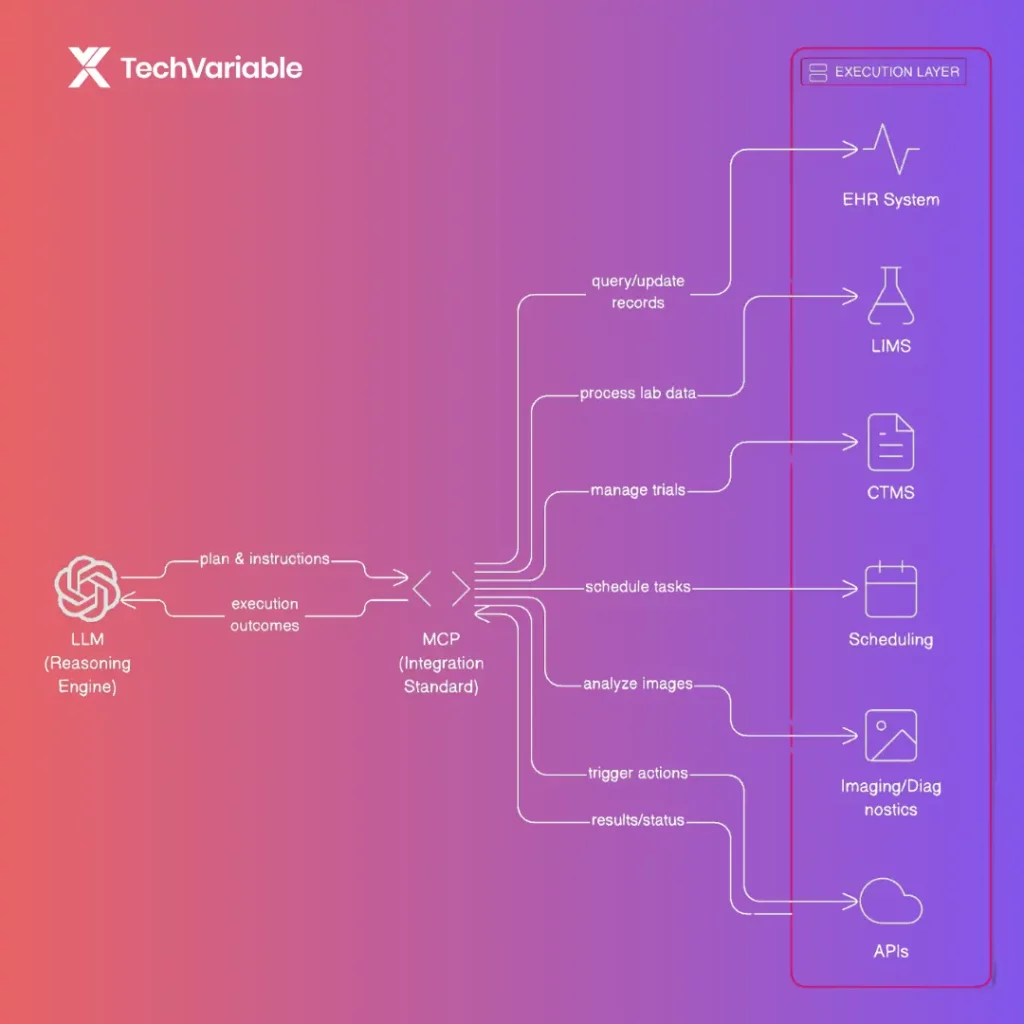
Unlike conventional generative AI tools such as ChatGPT, which focus on conversational outputs, agentic systems perform multi-step reasoning and take real actions. They can query databases, process medical records, schedule tasks, and trigger other systems automatically.
This is made possible through emerging standards such as the Model Context Protocol (MCP)—a framework that lets large language models (LLMs), APIs, and legacy software systems communicate seamlessly. Think of MCP as the healthcare industry’s “HTTP moment.” Once these standards are in place, AI systems can finally interconnect safely, enabling smarter, context-aware workflows across the entire healthcare data ecosystem.
In this architecture, LLMs act as the brain—understanding and planning—while APIs and legacy systems become the body, executing precise actions. Together, they create a connected network where AI agents in life sciences can collaborate across functions like R&D, clinical trials, and regulatory operations.
Transforming Healthcare and Life Sciences with Agentic AI
The potential applications of AI in healthcare are vast and growing rapidly. On the operational side, agentic AI can automate processes such as claims management, prior authorizations, and clinical documentation. This reduces administrative overhead, minimizes billing errors, and combats clinician burnout—all while improving patient outcomes.
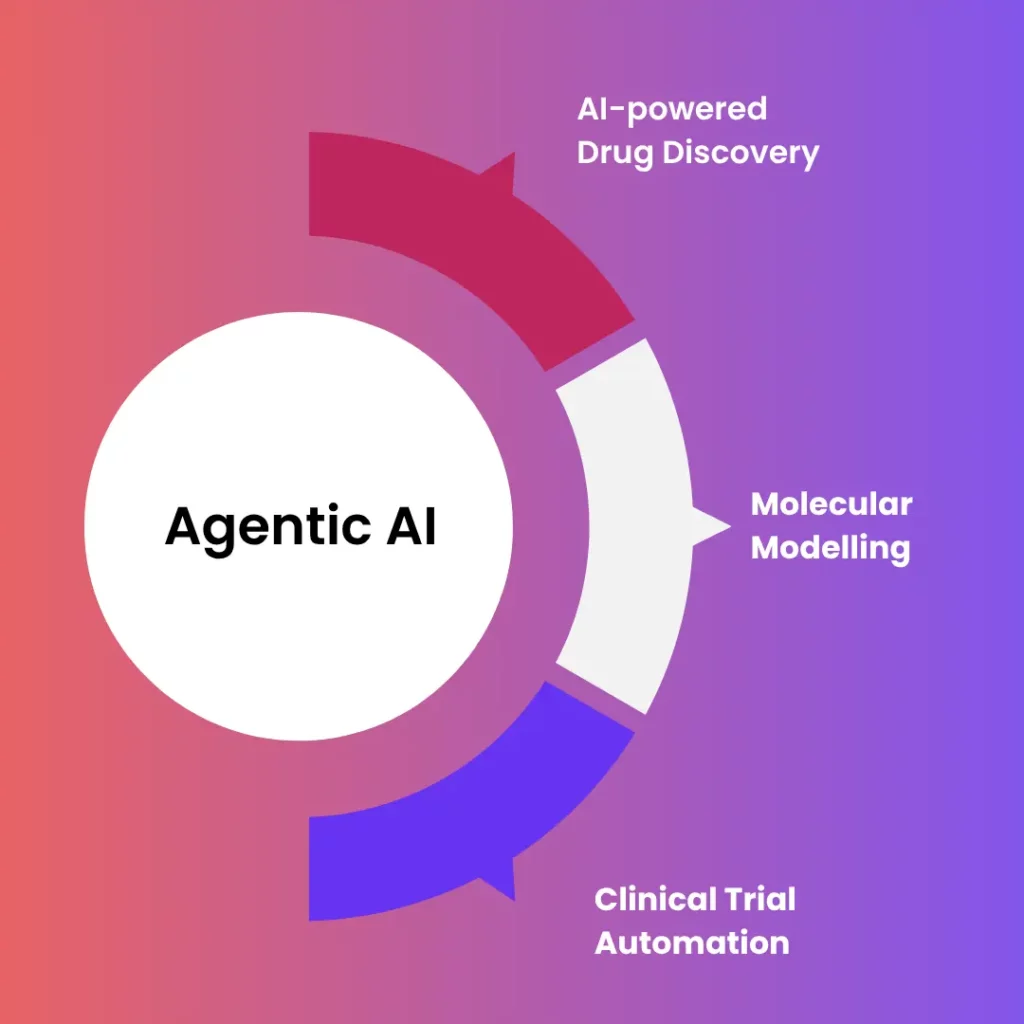
In life sciences, the transformation runs even deeper. Agentic AI is accelerating AI-powered drug discovery, molecular modeling, and clinical trial automation. It enables in-silico screening, real-time data analysis, and smarter orchestration of research studies.
Clinical trials, traditionally plagued by delays and inefficiencies, stand to benefit enormously. From patient recruitment and site coordination to data validation and regulatory submissions, agentic systems can orchestrate the entire workflow. Accenture estimates that agentic AI could unlock over $50 billion in economic impact across healthcare and life sciences in the next five years.
The Challenge of Accuracy and Clinical Responsibility
Despite its promise, AI in healthcare must operate under strict standards of accuracy, transparency, and clinical responsibility. When lives are at stake, “close enough” is never acceptable.
Modern AI models in life sciences now achieve accuracy rates approaching 90%, but the key is validation and oversight. Robust systems layer multiple safety checks: automated evaluations where AI cross-verifies AI (“AI-against-AI”), real-time transparency through dashboards and logs, and human-in-the-loop supervision at critical decision points.
As these systems mature, the role of experts shifts from performing every step to managing and validating the work of AI agents—a model often described as “human-on-the-loop.” This structure preserves accountability while scaling efficiency.
The Democratization of AI Development
Perhaps one of the most profound cultural shifts happening now is the democratization of AI development. With tools like ChatGPT familiarizing millions with conversational AI, more professionals—especially those who are “tech adjacent”—are beginning to experiment with automation.
These may be data scientists, innovation leads, or IT business partners who understand their domain deeply but are not software engineers. Using low-code AI platforms, they can now build tailored solutions, automate analytics, and deploy AI agents customized to their team’s needs.
The result is a distributed innovation model, where ideas come not just from the IT department but from across the organization. This movement is crucial to achieving AI adoption in healthcare at scale.
Escaping Pilot Purgatory
One of the most common pitfalls in enterprise AI initiatives is “pilot purgatory”—a state where promising proofs of concept never make it to production. Many projects stall because they fail to demonstrate tangible business value or depend heavily on manual integration.
Agentic AI offers a way out of this cycle by producing applications that are production-ready from day one. When users can deploy, test, and refine directly within secure, compliant frameworks, organizations can transition seamlessly from experimentation to enterprise adoption. True value emerges only when AI systems integrate smoothly into daily workflows.
The Next 24 Months: Where the Impact Will Be Most Visible
In the near term, the most visible impact of Agentic AI in healthcare will be in areas with repetitive, data-intensive processes—such as clinical trial orchestration, patient data management, and drug safety monitoring. Early successes are also expected in customer engagement, medical affairs, and sales enablement, where AI agents can provide real-time insights and streamline communication.
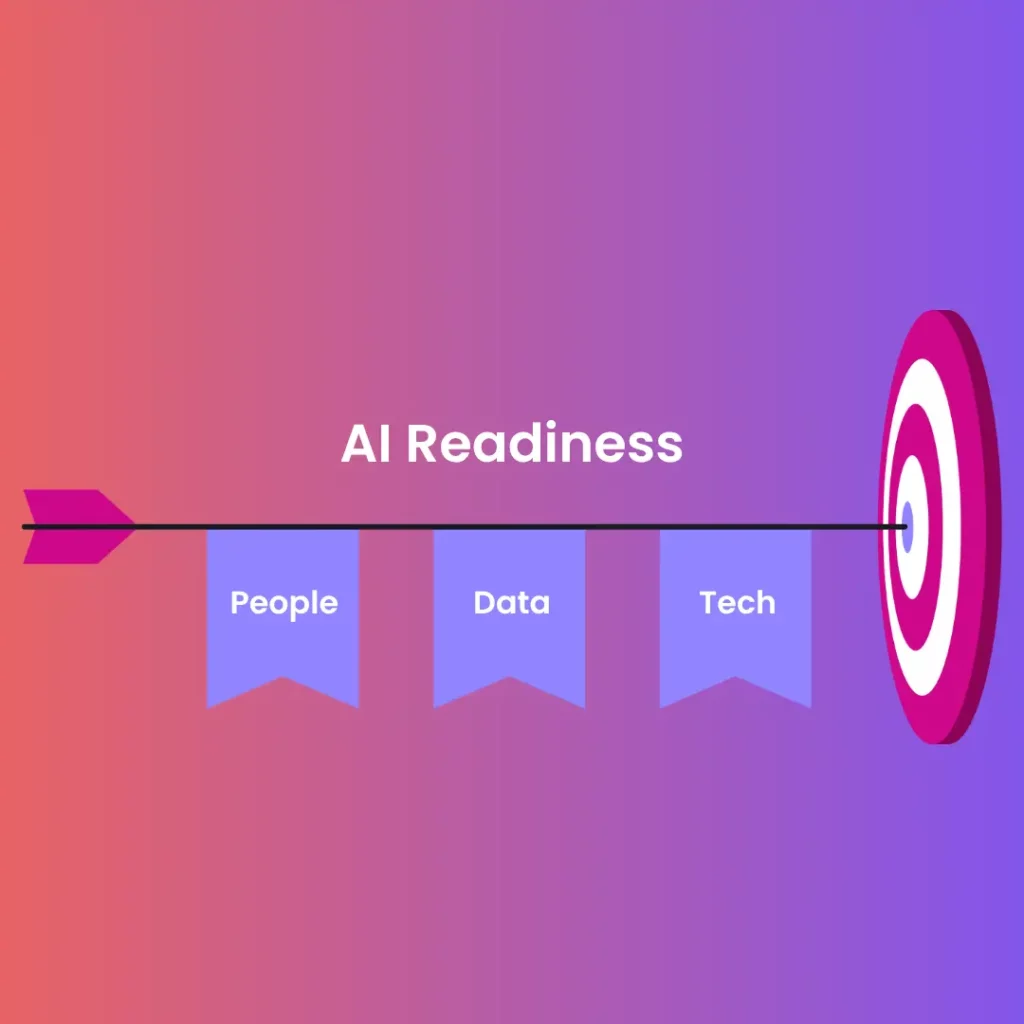
Over the next five to ten years, AI agents are likely to evolve into genuine collaborators in scientific workflows—analyzing literature, designing experiments, and managing post-market surveillance. Reaching that future requires AI readiness across three pillars: people, data, and technology. Teams must be trained to work with AI; data must be standardized and governed; and systems must be interoperable and secure.
Preparing for Ethical and Effective AI Adoption
For digital health founders and enterprise leaders, the first step is mindset. Keeping an open mind, starting small, and involving stakeholders early can make the difference between another pilot and a scalable solution.
Focus on measurable outcomes, build for production from the start, and invest in workforce training and data governance. Ethical, transparent, and human-centric design will determine which organizations succeed in this new agentic era.
Preparing for Ethical and Effective AI Adoption
For digital health founders and enterprise leaders, the first step is mindset. Keeping an open mind, starting small, and involving stakeholders early can make the difference between another pilot and a scalable solution.
Focus on measurable outcomes, build for production from the start, and invest in workforce training and data governance. Ethical, transparent, and human-centric design will determine which organizations succeed in this new agentic era.
A Future of Human-AI Collaboration
Agentic AI is not here to replace people—it’s here to empower them. When combined with human expertise, transparent oversight, and robust engineering, it offers a blueprint for transforming healthcare from reactive treatment to proactive intelligence.
In the coming decade, AI in healthcare and life sciences will evolve from an experimental technology into a trusted partner in care delivery and scientific discovery. The journey from sick care to smart care has begun—and it’s powered by agentic intelligence.
discovery, and commercial operations like customer success and regulatory documentation. In five to ten years, the vision is that AI agents will move from assistant roles to true collaborators in scientific work—helping design experiments, synthesizing literature at scale, and managing post-market surveillance. Reaching that vision requires preparation on three fronts: people readiness, data readiness, and technology readiness. Workforces must be reskilled to work with AI; data must be standardized and governed; and systems must be capable of secure, auditable integrations.
If you’re an innovator or a healthcare leader thinking about where to start, the pragmatic advice is to keep an open mind, begin with low-hanging use cases, and engage stakeholders early. Experiment, yes—but do so with an eye toward adoption: measure outcomes, build for production, and prepare your teams for the change. Invest in the foundations—governance, observability, and training—so that when agentic AI reaches full maturity, your organization can adopt it safely and effectively.
Agentic AI is not a magic bullet, but it is a powerful new tool. When paired with human expertise and robust engineering, it offers a path toward a smarter, more efficient, and more patient-centered healthcare system—one where innovation translates into real-world impact rather than remaining stuck in pilot purgatory.
At TechVariable
We help payers and healthcare companies design and implement integrated data platforms, built on:
- FHIR-first architecture
- Scalable ingestion frameworks
- Smart data modeling
- Robust EMPI and semantic normalization
- HIPAA- and NCQA-compliant governance