An Ultimate Guide to EHR Integration
A patient’s electronic health record (EHR) stores their medical history digitally. Their diagnosis, medications, allergies, test results, and treatment plans are all described in detail on an EHR. These records are stored electronically, unlike traditional paper records, and may be viewed and shared securely by licensed healthcare practitioners.
EHR integration is essential for enhancing care delivery across many different domains. Patients are more proactive about their treatments when they have simple access to their own medical records. This improves medication compliance, which improves the course of treatment. Information sharing results in better decision-making and more economical healthcare, from a decrease in redundant testing to a more coordinated plan of care.
EHRs are essential for enhancing patient care, making healthcare delivery more effective, and enabling data-driven decision-making.
Some examples of EHR Integration
In order to store and manage patient information, many EHR systems are utilized by healthcare organizations. Do note that the features, functionality, and interoperability abilities of these systems vary.
EHR platforms that are widely used include those from Epic, Cerner, Allscripts, MEDITECH, and athenahealth. Each system has advantages and disadvantages, and healthcare organizations pick the one that best suits their needs and operational procedures.
The need to integrate EHRs
Integration of EHRs can have a positive impact on healthcare organizations. The push for interoperability in the healthcare industry is supported by EHR Integration . As a result, it is crucial for data exchange and improving healthcare in general.
With an EHR, you’ll have instant access to patient information, promote cooperation among your care teams, increase productivity, and enhance decision-making.
Messaging standards for EHR integration
Messaging standards in healthcare refer to the standardized formats, codes, and protocols for exchanging clinical and administrative data between healthcare applications from various suppliers. They make sure that information is communicated rationally and consistently, facilitating effective interaction across various healthcare apps and systems.
These guidelines simplify interoperability, ensure the secure transmission of medical data, and improve patient care.
Different messaging protocols used for healthcare interoperability
HL7
FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) is a modern and evolving standard for healthcare interoperability. FHIR employs APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) and web standards to organize and expand the flexibility of medical data transmission. Since it places a great emphasis on modularity, simplicity, and ease of use, it is the ideal choice for contemporary EHR integration projects.
Sample Message
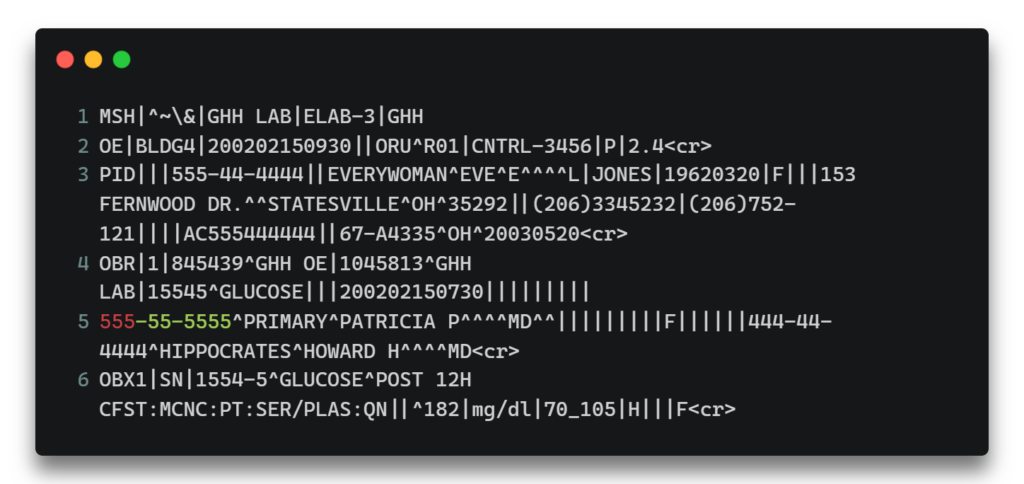
FHIR
FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) is a modern and evolving standard for healthcare interoperability. FHIR employs APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) and web standards to organize and expand the flexibility of medical data transmission. Since it places a great emphasis on modularity, simplicity, and ease of use, it is the ideal choice for contemporary EHR integration projects.
Sample Message

C-CDA
Using the C-CDA (Consolidated Clinical Document Architecture), an industry standard, healthcare professionals can share clinical information like discharge summaries, progress notes, and test results. C-CDA provides a set of templates and guidelines for structuring and presenting clinical information in order to guarantee consistency and interoperability when exchanging patient data across various EHR systems.
A comparative analysis of the three types of messaging protocols
| HL7 V2 | FHIR | C-CDA |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | ||
| Focuses on issues with healthcare interoperability. | Used for internal system communication in healthcare facilities. | A markup standard for documents that outlines the format and semantics of clinical documents. |
| Function | ||
| It specifies a structure for sending health-related data. | It stands for certain clinical concepts that can be used to solve issues in healthcare and related processes swiftly and effectively. | It contains information that meets ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) Continuity of Care Record (CCR) standards. |
| Specificity/Use-case | ||
| Supports the bulk of the widely used interfaces in the global healthcare sector. | Supports RESTful architectures and seamless message or document-based information exchange. | Supports the sharing of clinical documents amongst those involved in a patient's care. |
| Messaging structure | ||
| Texts, pipes, and hats are the components of an HL7 V2 message. | Using an HTTP request/response, transactions are carried out directly on the server resource. Each resource contains extensions, narratives and structured codes. Communication is executed via RESTful APIs and is represented in XML and JSON formats. | CDA is based on the XML format. |
Challenges in EHR integration
Data Privacy
One of the main issues with digitization is privacy. The integration of EHRs can raise similar issues. There is a lot of private and sensitive data in the system. According to the most recent study, healthcare records are vulnerable to data breaches.
Solution: A special focus should be placed on the security measures used when integrating your EHR. Choose HIPAA-compliant solutions that are cloud-based to protect all the data and provide the highest level of security.
System non-compatibility
If you choose to integrate EHR, be prepared to deal with interoperability issues. The capacity of your hospital’s EHR to work with other systems is crucial. Since the majority of hospitals use different systems, compatibility issues may arise.
Solution: To find out if your systems are compatible with the future EHR you develop, speak with your software development partner. They can provide you with a plan that will lessen the hazards. Contact Us
Staff training
Be ready to deal with interoperability difficulties if you decide to integrate EHR. The ability of the EHR at your institution to communicate with other systems is essential. Compatibility problems could occur because the vast majority of hospitals employ various systems.
Solution: Ask your software development company to commit their time and resources to help migrate to a new system and to offer additional training so that future EHR users won’t have any questions. Consider writing a manual that colleagues may use as a reference.
Workflow interference
The introduction of EHR can seriously disrupt existing workflows in healthcare organizations that continue to rely primarily on paper documentation. Not all hospitals have enough computers to give each doctor the necessary gear, which is another potential issue.
Solution: Setting up the workflows must take EHR installation into consideration. It’s likely that you will need to make several adjustments to them as well as update records to make everything work with the system you intend to implement.
Cost of EHR integration
The cost of deploying an HL7 application can vary significantly based on a number of variables, including the programme’s size and complexity, the project’s scope, the technology employed, the degree of customization necessary, and the development team’s level of experience.
Some HL7 applications could be fairly straightforward, like a straightforward message parser or validator, whilst others might be more complicated, like a fully functional clinical information system. Additionally, whether you decide to employ open-source software or for-profit off-the-shelf solutions may affect how much it costs to construct an HL7 application.
Implementing an HL7 application often costs between a few thousand dollars and several hundred thousand dollars or more. You may reach us at TechVariable to get familiar with HL7 standards and healthcare technology to acquire a more precise estimate of the price of your HL7 application.
Benefits of EHR integration in health data system
Data acquisition
EHR integration utilizes integrated data lakes to extract the data from the integrated EHR system by examining databases, flat files (CCDA, CCLF, XML, CSV), HL7 interfaces, and other web services.
Ease in data entry
One platform for all your patient data can facilitate a smooth clinical experience and speed up communication about care plans. Patients can receive a streamlined experience from medical and dental experts that includes sensitive patient data collection, evaluation, and transfer.
Cost reduction
Cloud-based EHR platforms cost next to nothing up front. While cloud EHR may require less infrastructure, client-server EHRs will involve clinic purchasing, regular monitoring, and testing of hardware.
Enhanced patient output
EHR is evolving as a channel for better interaction between patients and healthcare professionals. In fact, patients can use personal health records (PHR) to update their own EHRs.
Conclusion
The present healthcare delivery model must be improved, and EHR integration is the way to do it. Structured and unstructured healthcare data from multiple data storage systems, including file servers and relational database management systems, are combined through data integration. True interoperability and successful EHR integration have many advantages, including improved patient care initiatives, decreased clinical errors, and improved care coordination efforts. True integration builds a robust and valuable collection of data that is essential for conducting population monitoring and public health research to spot issues in real time.
Download the ultimate guide to EHR INTEGRATION
EHRs have revolutionized how stakeholders manage, share, and access patient healthcare records.








