FHIR vs HL7
Did you know that medical errors due to lack of effective communication among healthcare providers are a leading cause of death in the United States? Therefore, cohesive communication among healthcare providers is crucial to ensure patient safety and prevent medical errors. To address this problem, healthcare interoperability, supported by standards like HL7 (Health Level Seven) and FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) comes into the picture.
console.log( 'Code is Poetry' );

In this blog, you will explore the significance of HL7 & FHIR in the healthcare sector for maintaining interoperability, along with why FHIR is a better option for healthcare.
Health Level Seven comprises various standards and messaging protocols, among them are HL7 version 2.x and HL7 version 3. Widely used – HL7 version 2.x enables healthcare settings to exchange clinical and administrative data promptly.
On the other hand, the newest set of standards, FHIR, is designed to be more user-friendly, prioritizing interoperability for the easy transmission of healthcare information. It works on a web-based framework, making it more accessible for healthcare stakeholders, software developers, and healthcare systems.
Evolution from HL7 to FHIR
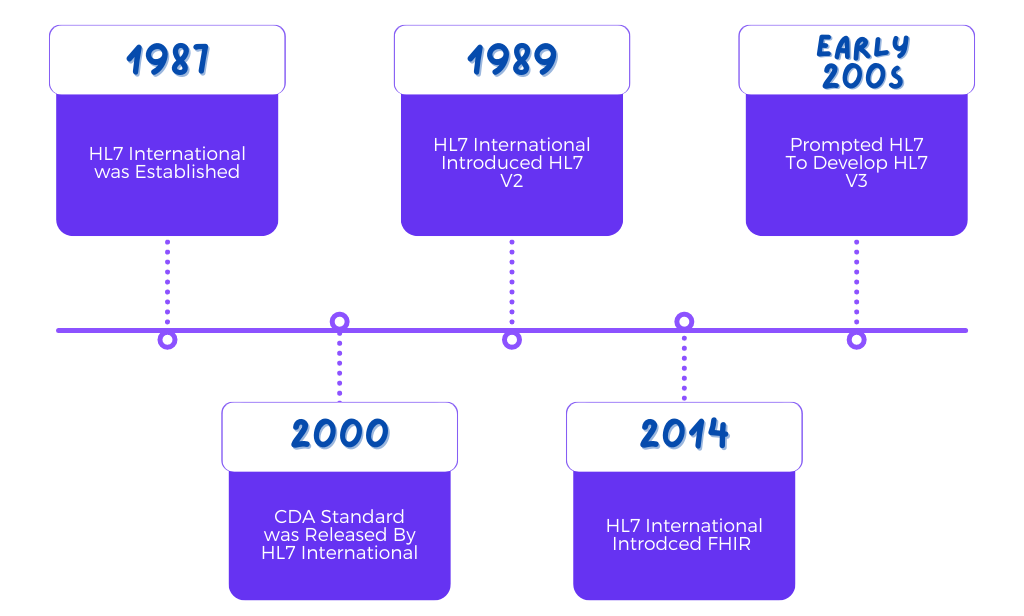
- In the year 1987, a significant milestone was achieved with the establishment of Health Level Seven International (HL7). Their ambitious objective was to create standardized healthcare data interoperability on a global scale.
- Building upon this foundation, HL7 introduced HL7 V2 in 1989, a standard that aimed to ensure seamless interoperability at an enterprise level across the healthcare industry.
- However, as the early 2000s unfolded, the importance of data in facilitating clinical and medical workflows experienced exponential growth. It became increasingly evident that the HL7 V2 data model was lacking in the necessary methodologies and resources to keep pace with the rapidly evolving healthcare landscape.
- HL7 swiftly recognized the limitations of the HL7 V2 data model, which prompted the development of HL7 V3. This new messaging standard, built upon XML coding, was designed to be more comprehensive. Regrettably, due to its lack of backward compatibility with HL7 V2, it did not achieve widespread popularity.
- Just two years after the release of HL7 V3, the organization unveiled the Clinical Document Architecture (CDA) standard.
- CDA was specifically designed as a simplified version of HL7 V3, employing an XML-based markup standard that facilitated the easier exchange of clinical documents.
- Recognizing the limitations of previous standards, HL7 embarked on the development of Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR).
- In 2014, HL7 introduced FHIR as a universal and simplified healthcare interoperability standard.
Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) acts as a common language for interacting with different computer systems and sharing data information securely.
Designed specifically for clinical data exchange, FHIR has become the leading framework in the field. Its versatility is particularly notable when working with emerging healthcare use cases such as mobile health applications, patient portals and data exchange between multiple healthcare organizations.
Unlike the previous HL7 versions, data transfer using FHIR is made possible via small units known as “resources” that hold vital information such as patient details, lab test results, drug prescriptions and allergies. These resources are smartly organized to ensure smooth accessibility and comprehension by different healthcare systems.
Healthcare interoperability is made much simpler, allowing healthcare providers to efficiently exchange clinical data with the transition from HL7 to FHIR.
To learn deeper into the workings of HL7 and FHIR, read this previous article from our blog: https://techvariable.com/blogs/hl7-and-fhir-significance-in-healthcare/
Thus, FHIR and SMART are meant to maintain the industry benchmarks of data access and data.
5 Key features of FHIR
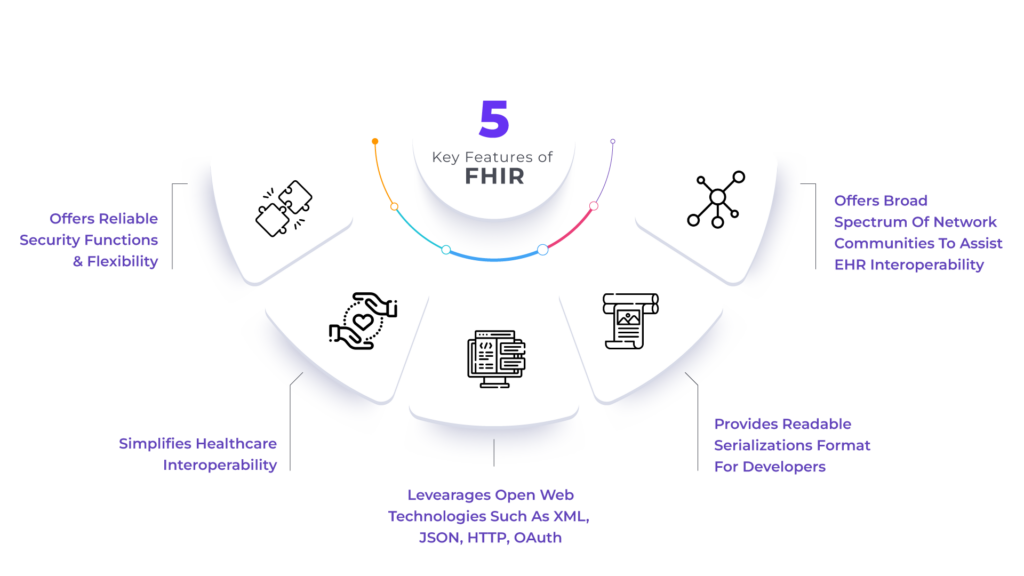
As stated earlier, it is a framework that enables the development of secure and interoperable healthcare apps. This is a platform-agnostic standard, i.e., it runs on any combination of operating systems and underlying processor architecture.
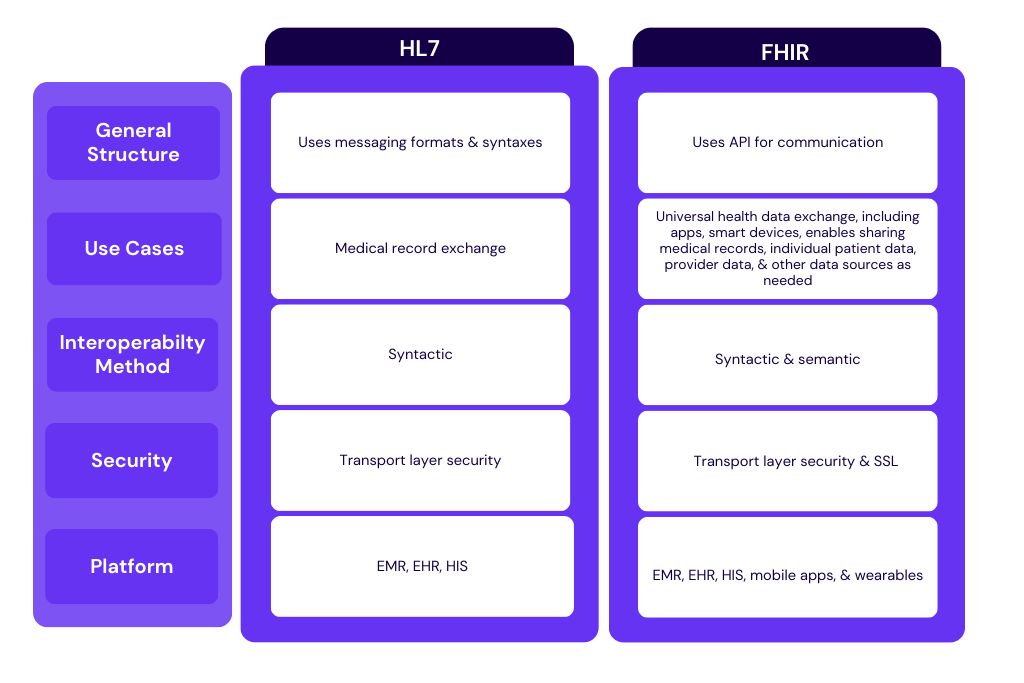
Difference between HL7 & FHIR
Although both these standards are developed and released by Health Level Seven International and belong to the same family of HL7 standards, there are some differences between them.
The main difference between FHIR and HL7 is that FHIR leverages RESTful web services and open web technologies such as XML, JSON, and RDF data formats, while HL7 only supports XML. The major advantage of the RESTful approach is that it accelerates interoperability between not just Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems, but also other devices and systems, including mobile apps, mobile devices, and wearables.
Let’s explore some other differences between the popular HL7 V2 and HLF FHIR:
Why FHIR is a better option than HL7?
Firstly, FHIR supports web-based technologies and can be used on any mobile device. Its focus on interoperability enables seamless data exchange between different healthcare systems. Its web-based APIs enable real-time access to patient data, facilitating smoother workflows and better coordination of care across different providers and organizations.
Secondly, it is not only easier to adopt due to its simplicity & flexibility, but also offers user-friendly access to quality information for app development.
FHIR sets itself apart from HL7 by aiming to facilitate coordinated care plans across different systems using mobile devices and easily accessible apps. It achieves this by allowing the integration of apps into the core operating system of EHRs, enabling seamless information flow into the provider workflow. In doing so, FHIR seeks to address the challenges associated with document exchange by streamlining the process and improving efficiency.








